Author- Pushpak Kale (Cloud Engineer)
 Azure ARC enabled Kubernetes
Azure ARC enabled Kubernetes

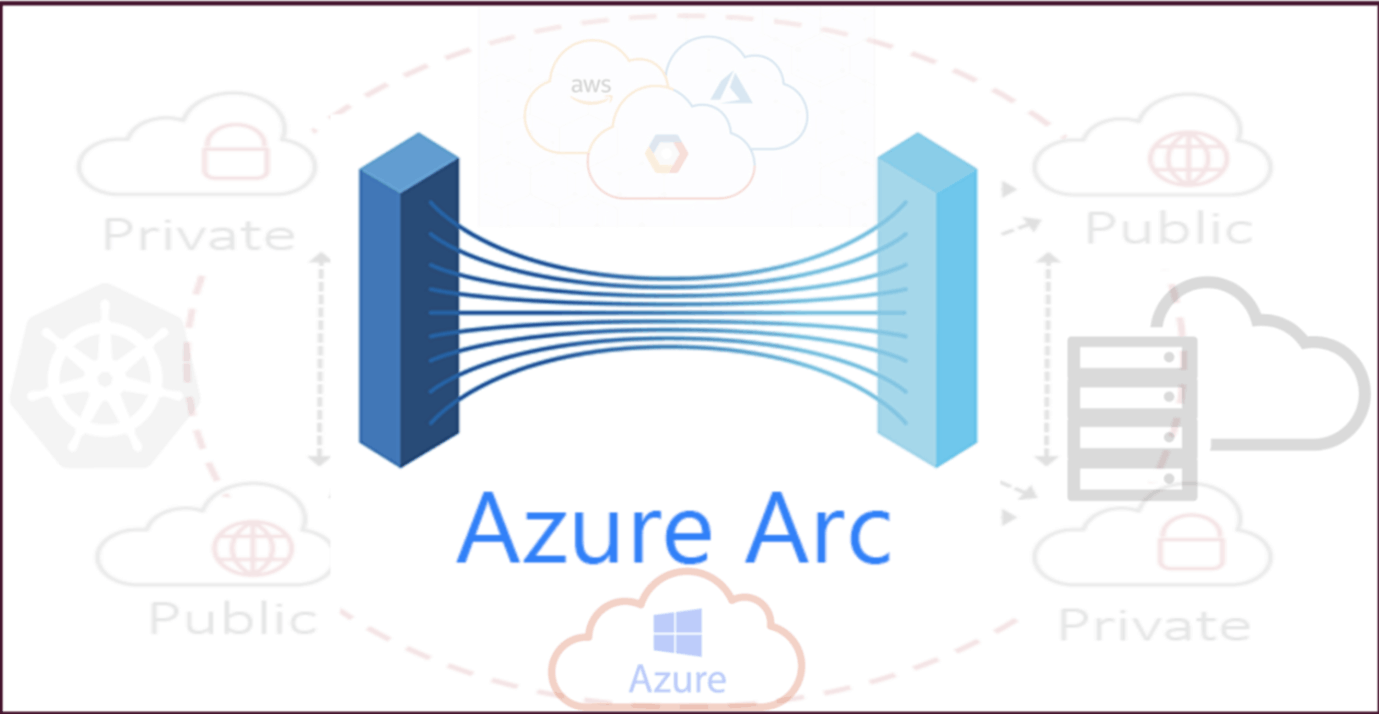
What is Azure ARC?
Microsoft Azure ARC is a unified management platform that simplifies operating complex and distributed environments across on-premises, edge, and multi-cloud. Azure ARC is designed to extend Azure management to any infrastructure. Azure Arc is an emerging hybrid cloud solution that lets users’ provision and manage virtually any server or database–whether it is a legacy Linux server running on-premises, a database hosted in the Microsoft Azure cloud or even a Windows virtual machine running in a competing public cloud, like AWS-using the Azure cloud’s native tooling.Features of ARC
ARC enabled Server Azure ARC enabled servers allows you to manage your Windows and Linux servers hosted outside of Azure, on your corporate network, or other cloud provider consistent with how you manage native Azure virtual machines. When a hybrid machine is connected to Azure, it becomes a connected machine and is treated as a resource in Azure. When an external machine is connected to Azure ARC enabled server, it enables the ability to perform the following configuration management and monitoring tasks:- Assign Azure Policy guest configurations using the same user experience as policy assignment for Azure Virtual Machines.
- Report on configuration changes about installed software, Microsoft services, Windows registry and files, and Linux daemons on monitored servers using Azure Automation Change Tracking and Inventory.
- Monitor your connected machine using Azure Monitor for VMs.
- Simplify deployment using services like Azure Automation State Configuration and Azure Monitor Log Analytics workspace for your Non-Azure Windows or Linux machines.
- Use Azure update management in Azure automation to manage operating system updates for your non-Azure Windows and Linux Machines.
- Use Azure Security Center for threat detection and proactively monitor for potential security threats
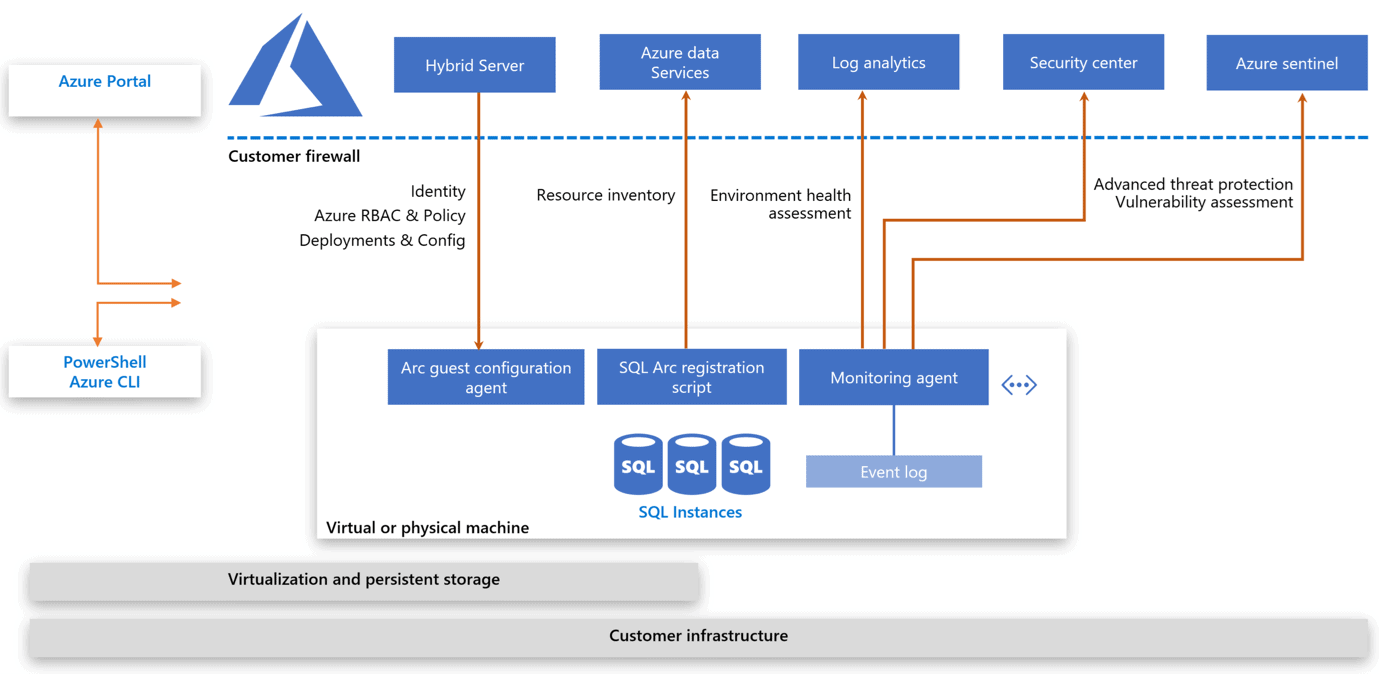
- Azure ARC enabled SQL server is a part of the Azure ARC for servers. It extends Azure services to SQL Server Instances hosted outside of Azure in a datacenter, on the edge or in a multi-cloud environment.
- The SQL Server can be installed in a virtual or physical machine running Windows or Linux that is connected to Azure ARC via the connected Machine agent. Customers now have the flexibility to deploy Azure SQL Database and Azure Database for PostgreSQL Hyperscale where they need it, on any Kubernetes cluster.
- From the Azure portal, customers get a unified and consistent view of all their Azure data services running across on-premises and clouds and can apply consistent policy, security, and governance of data across environments.
 Azure ARC enabled Kubernetes
Azure ARC enabled Kubernetes
- Azure ARC enabled Kubernetes lets users connect Kubernetes cluster running on-premises or any other cloud provider with Azure for a unified management experience.
- ARC provides a single pane of glass operating model to users for all their Kubernetes clusters deployed across multiple locations and platforms.
- ARC provides capabilities of Azure management to the clusters, unlocking Azure features like Azure Policy, Azure Monitor and Azure Resource Graph. By attaching an external existing Kubernetes clusters to Azure, users can use all the features to control external clusters like any other internal Azure resource.
- To connect a Kubernetes cluster to Azure, the cluster administrator needs to deploy agents. These agents run in a Kubernetes namespace named azure-arc and are standard Kubernetes deployments.
- The agents are responsible for connectivity to Azure, collecting Azure Arc logs and metrics, and watching for configuration requests.
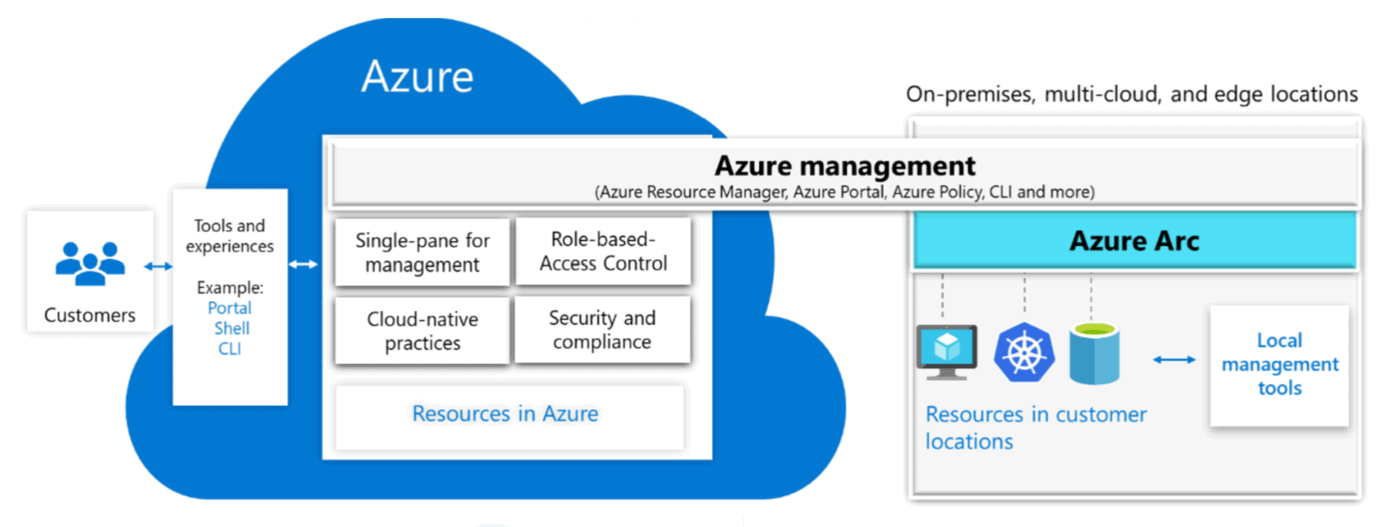
Working of Azure ARC

- With Azure ARC clients can mix and match physical servers, VMs and Kubernetes clusters within the hybrid environment.
- This means, workloads running in multiple clouds such as Azure, AWS, Google, workloads running on-premises in Azure Stack or other hardware, as well as services running at the edge. Consider all the services currently running on-premises and in the cloud across organizations today – Kubernetes Clusters, Data Services, Windows, and Linux Servers etc.
- Azure ARC’s key differentiation lies in the balance between traditional VM-based workloads and modern containerized workloads that operate in the same context of the hybrid and multi-cloud environments.
Benefits of Azure ARC
- Unified approach to managing environment – Businesses can manage their public cloud resources running within and outside Microsoft Azure through the same centralized management with the help of Azure Resource Manager, Microsoft Azure Cloud Shell, Azure Portal, API and Microsoft Azure Policy.
- Build Containerized Applications – Applications are deployed, configured, and managed uniformly using GitOps based configuration management.
- Cloud Security – Businesses can leverage compliance and security capabilities of Azure Security Center for all Cloud resources – within Azure and external.
- Organize all your servers – Govern all your servers that sit on-premises, on other clouds or at the edge the same way that you govern your Azure Servers.
- Run Managed Services – ARC can run managed service successfully in a hybrid and multi-cloud Environment.











